Making a router cuts down on the Internet speed. Why the router slows down Wi-Fi speed and how you can increase it. Channel Width Setting
A wireless Wi-Fi access point has not been an innovation for a long time; almost every apartment uses this method of obtaining Internet access for devices. But sometimes it happens that the device starts to work incorrectly. One of the most common problems that users may encounter is the router. What to do if this happens? Let's try to understand the reasons for this malfunction and consider ways to solve this problem.
This device is otherwise called a router. The main function is to distribute wireless access to the Internet via radio communication. Routers use the 802.11 communication standard to operate. Depending on the model, the operating range may vary, as well as the data transfer rate.
The device itself is represented by a small case, connected antennas and a power supply for recharging the device. The range of the Wi-Fi network also depends on the technical characteristics of the router. Devices intended for home use create a network with a radius of 10-15 meters. The Internet source is a local network, which is synchronized with the router by wire.
Technical characteristics of the router model

If you notice that the router produces poor performance, then pay attention to the technical characteristics of this model. The theoretically possible speed limits indicated on the box are always far from the real numbers. If the manufacturer claims that the maximum speed is 150 Mbit/s, then in practice you will get 20-30 Mbit/s.
The most important performance parameters are the following:
- Transmitter power. The possibility of waves passing through walls depends on this parameter. Routers with a weak transmitter, as a rule, do not provide a strong signal in remote rooms of the premises.
- Receiver sensitivity. Some manufacturers do not even indicate this parameter in the list of technical characteristics of router models. The importance of this indicator is as follows: if the signal level is poor, the connection will not be interrupted. It is better to choose models with a sensitivity parameter of -92, -94, -98.
- Number and type of antennas. The number of antennas does not always indicate greater performance of the router. If the antenna gain is 5 dBi, and the number of antennas is at least 2, then such a router can easily cover an entire apartment or one-story house with a network.
- Antenna gain. The higher the coefficient, the more energy goes to the sides, and less up and down.
Routing speed
The data transfer speed over a Wi-Fi network will always be lower than a wired connection. This is because wireless communications are less stable and radio waves constantly overlap and overlap each other, causing interference. The result of this is a decrease in data transfer speed.
The figure declared by the manufacturer, which is written on the router box, is very far from the practically achievable speed level. The theoretically achievable speed is determined under ideal environmental conditions. The throughput of the real environment decreases significantly due to the presence of various interference and the action of other devices. To roughly determine the maximum possible data transfer speed, you need to know the parameters of the router. Let's give an example: an 802.11n network with a theoretically possible speed of 150 Mbit/s gives a practical maximum of 50 Mbit/s.
Reasons for the drop in connection speed

If you notice that it is different than with a wired connection, it means that the router is slowing down the data transfer for some reason. There are several common reasons why a router slows down Wi-Fi speed.
- The software is out of date. An out-of-date firmware version may reduce the performance of the router.
- The settings are made incorrectly. The choice of communication channel or network standard depends on the router model.
- The router model is outdated. The ability of the transmitter in the router to operate at high speeds depends on what communication standards the model is designed for.
- The device model is outdated. The same situation is with the hardware. If you connect a laptop to a Wi-Fi network that is designed for the 802.11g standard, and the router runs on 802.11n networks, then the data transfer speed will be significantly reduced.
- A large number of connected devices. If you connect many devices to one access point, don't be surprised that the speed will drop significantly. The speed is especially severe when downloading torrents.
- Remoteness of the router. The drop in speed in remote areas of an apartment or house can be explained by the limited range of the router. Are you wondering why your router slows down? If the device is separated from the connected device by several walls, then a decrease in speed is normal.
How to check connection speed?

The data transfer speed from the router to all devices is measured in KBit/s or MBit/s. To measure speed, you can use special programs that are installed on a device connected to a Wi-Fi network. An alternative option is online services, with which you can also check your Internet speed.
If you want to get a reliable result, then before taking measurements you need to disconnect all other devices from the network and configure the router correctly. To determine the performance of the router, first measure the speed of the wired connection, and then the speed over the Wi-Fi network. You can check your Internet speed using servers such as Speedtest, Speed.yoip, etc.

Correctly specifying the parameters in the personal account menu will change the capabilities and performance of the device. Let's try to figure out how to configure it so that the router does not slow down its speed. We list the most significant indicators for correct operation:
- Channel selection. There are a total of 13 communication channels that routers use. When connected, each device sees several routers that are located at its neighbors. To avoid connection failures, you need to select one channel that is least used by neighboring routers.
- Signal strength. In most cases, standard settings assume reduced signal strength. Set the maximum value. This will improve transmission in cases where you constantly move around rooms with a mobile device.
- Channel width. In most router models, the frequency range can vary from 20-40 MHz. The highest channel width gives a significant increase in speed only if there is good reception. If reception is poor in distant rooms, then increasing the channel width will not help you. Select a channel width of 20 MHz in the router settings and measure the speed, then do the same with the 40 MHz parameter. We leave a more stable option.
- Security mode. We select the most reliable WPA2 mode. If you use WEP, WPA or TKIP, then the router automatically reduces the Internet speed to 54 Mbit/s.
How to increase data transfer speed over Wi-Fi?
The first step is to update the router firmware. To do this, go to the official website of the manufacturer of your equipment and download the latest firmware there. You can determine which of them is the most current by the update date and serial number.
The next step will be setting up the router. You can select the necessary parameters through your router’s personal account. The box contains an IP address that you need to go to to enter all the necessary settings.
You need to choose the right location for the router. Take into account the fact that the network will be evenly distributed only when the router is installed in a place that is the same distance from the extreme points of the room. Even if you have made all the settings correctly, but the transfer speed is low, pay attention to the fixation of the access point and the layout features. Passing a signal through several walls will significantly reduce the speed.
Updating the router firmware before use

Why update your router firmware? The thing is that manufacturers periodically release new software for their products in order to increase equipment performance, correct errors in previous versions, optimize operation in modern networks, and improve some functions.
You can update the device yourself without the help of specialists. To do this, you need to connect the router to the computer via a cable and disconnect the connection from the provider. Throughout the entire firmware process, the router must be turned on.
Download the latest firmware from the official website, unpack the archive on your computer. Log into your router’s personal account via your IP address and find the update category in the menu. Select the firmware file from the menu and the update process will begin. Once the download is complete, the router will restart. The installation of the new software is complete.
Choosing a productive router

The most important factor when choosing a router will be its future application. If you are choosing a router for home use, then you can limit yourself to an inexpensive model. Pay attention to the inputs: the router must be able to connect wired and wirelessly.
Be sure to study the characteristics of the models. Consider parameters such as transmitter power, antenna sensitivity, number of antennas and their gain. If you decide to purchase a productive device, then choose a model that operates in the frequency range of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. This band is less congested by other devices, so the data transfer speed will be faster. Regarding the quality of the router, you need to consider the following: beware of cheap Chinese devices, choose time-tested brands.
Device Compatibility
If you notice that the data transfer speed on some of your devices is slower than others, or the connection cannot be established, then there is most likely a hardware conflict.
Sometimes it happens that synchronization causes problems due to incompatible devices. The latest modern computer will not be able to connect to an outdated router and vice versa. The problem lies in the standards and operating frequencies supported by the devices. If the router transmits a signal at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, and the device is designed for an operating frequency of 2.4-5 GHz, then the operation may be incorrect, or synchronization will not be established at all.
There is only one solution to a hardware conflict - replacing the hardware. An older model of transmitter or receiver will have to be replaced with a new, more modern one.
Finally
Before throwing away your old router, which has served you faithfully for a long time, try to figure out the reasons for the drop in speed. Perhaps, after setting the parameters correctly, the router will stop slowing down the speed, and the performance of your devices will normalize.
I decided to write an article and express my opinion and some observations about routers that do not reduce the speed and provide a stable 100 Mbit/s over Wi-Fi networks, or the speed that is stated according to the tariff of the Internet provider. A very controversial, controversial and popular topic. After all, everyone who chooses a router is mainly looking for a model that does not reduce speed. Or one that “breaks through walls.” But that’s a different story :)
The backstory is very simple. Most likely, you yourself have seen and seen from your own experience how routers reduce speed. Or somewhere on the Internet, perhaps in reviews of a particular router, they read a comment about how a certain “deceived” client used the Internet at maximum (according to the provider's tariff) speed, and then I bought this damn router, configured it, and the connection speed dropped several times. Perhaps he still gets almost maximum speed via the cable from the router (for example, 100 Mbit/s), but Wi-Fi is absolutely terrible. The speed dropped to 50, 20, 10 Mbps or even less.
This is exactly the “problem” that almost everyone who connects their devices to the Internet via a Wi-Fi network faces. Yes, the connection speed via the Wi-Fi router drops. How much depends on many factors, which I will discuss in this article. The router is not always the only one to blame. And most importantly, there is no router that does not reduce Wi-Fi speed. It’s just that some cut less, some cut more. Under different conditions and external factors.
Why did I write 100 Mbit/s in the title? Because this is the most popular tariff, which is most often connected in cities. Yes, the speed at the tariff may be lower. In this case, you may not even notice a drop in speed after installing the router. For example, if your provider gives you up to 20 Mbit/s. But there are tariffs with speeds up to 200 Mbit/s, 500 Mbit/s or even more. In this case, the loss in Internet connection speed after installing the router can be very large. Here, of course, a lot depends on the router you choose.
Why is the speed lower than what is stated on the box with the router and in the specifications?
But why? Why does the box with the router say N150, N300, N450, or even N600 and higher, but my Internet speed is so low? Support workers of online stores, router manufacturers, or innocent consultants in stores very often suffer from approximately this question :)
Now I’ll explain, and we’ll close the topic with these numbers, which are indicated on the box, or in the specifications for the router. Also, many people see the “Speed” item in the connection properties on a computer or mobile device, and do not understand why the data is so different.

Each router has a certain Wi-Fi network speed index. This is one of the main indicators and criteria when choosing a router. If we consider routers that operate only in the 2.4 GHz range, then the speed there is from 150 Mbit/s, and apparently up to 600 Mbit/s (4 antennas). If we consider dual-band routers that support 5 GHz frequency, then the speed will be higher.
So, all these numbers, up to 150Mbps, up to 300Mbps, are the maximum theoretically possible wireless network speed that this router can produce under ideal conditions and only in theory. In some article I already wrote that these numbers have nothing to do with actual speed, since it depends on many factors.
For example: an 802.11n router that can deliver speeds of up to 300 Mbps (there are most of them on the market now) in theory, in reality it can squeeze out a maximum of 100 Mbit/s. But this is also practically impossible. I'm not even talking about budget models with the N150 index. There is a maximum of 50 Mbit/s.
It turns out that if you have a tariff of 100 Mbit/s, and you bought a router with a speed of up to 150 Mbit/s, then the maximum you can get via Wi-Fi is 50 Mbit/s.
Don't forget that Internet speed primarily depends on your provider. From the tariff. Therefore, before complaining about a slow connection through your router, connect to the Internet (cable from provider) directly to the computer and . Then you will have data to guide you.
The speed also depends on the device itself that you connect to the Wi-Fi router. From the strength of the wireless network signal, from interference, and to some extent from the wireless network settings.
What causes the speed through a Wi-Fi router to drop?
Now about the most important thing. Why is the speed directly the same as stated by the provider, the cable from the router is the same, or slightly lower, but the speed sags over Wi-Fi. Sometimes even very much.
Here, as if without complicated proceedings, everything is clear. A cable is a cable. According to it, our Internet “flies” to devices strictly along the designated route, and is not scattered throughout the room, apartment, etc., as is the case with Wi-Fi.
Let's take a closer look and look at the main factors that cause wireless connection speed to drop.
- I'll tell you a little secret. A router is like a small computer. It contains the main board, processor, RAM, permanent memory, and wireless module. As with a computer, the performance of a router depends on the amount of memory, processor performance and the quality of these elements. The more memory, the more powerful the processor and wireless module, the faster the router can process data. And the speed of the Internet and the stability of work even under load directly depend on this. It often happens that the speed seems to be good, but as soon as a load appears on the router, it immediately sags. All this is due to weak and not very high-quality hardware, which is most often installed in budget models.
- If our computer runs on Windows, then the router also runs on its own operating system. In other words, firmware. And a lot also depends on the firmware. If the software part is done poorly, then even powerful hardware will not save you. And if the firmware has many errors, is crude and unfinished, then the connection speed may also suffer because of this. Always update the firmware on your router. This does not always have a positive effect, but it happens that the router starts working better and faster. You need to update the firmware!
- Each provider uses a specific type of Internet connection. If you set up a router yourself, then most likely you understand what I mean. So, Dynamic IP (DHCP) and Static IP are the simplest and lightest protocols. With them, the router will reduce the speed least of all. If the connection is PPPoE, then this is more complicated, the router will waste its resources to connect via this protocol and the speed will drop. And in the case of PPPTP, the speed will drop even more.

So it’s better to choose a provider that provides addresses automatically, or requires you to enter them manually, but without authorization using a username and password. - Wi-Fi client. Simply put, the device that you connect to the router. For example, when measuring speed from a laptop (via Wi-Fi), it may be 15 Mbit/s, and from a phone – 70 Mbit/s. Or vice versa. Why is that? It's very simple, the speed is limited by the slowest device on the network. And if the router gives even 100 Mbit/s, and the module in a laptop or other device has a limit of 24 Mbit/s (this is the maximum real speed for 802.11g), then this is the speed we will get. An outdated Wi-Fi module, lack of support for new standards and technologies, outdated software (drivers) - all this directly affects the speed of your Internet connection. And the router, as you understand, has nothing to do with it.
- Other external factors. For example, the poorer the signal strength on your device, the slower your connection may be. Each Wi-Fi network operates in a certain range and on a certain channel. And when there are many of these networks around, they begin to intersect and interfere with each other. I would also add here interference from various household appliances, obstacles in the form of metal in the walls, etc.
- Router settings. From the factory, by default, the router is configured to ensure maximum compatibility with different devices. Including old ones that you may not have. For example, the network operating mode is set to auto mode (b/g/n). And the channel width is 20/40 MHz. But, if you don’t have older devices that only support g wireless network mode, then it makes sense to switch the router to n (only n) mode, and the channel width to 40 MHz.
 Perhaps the speed of the Wi-Fi network will increase significantly. All these settings can be changed in the router’s web interface, in the section with wireless network settings. I wrote about this in an article.
Perhaps the speed of the Wi-Fi network will increase significantly. All these settings can be changed in the router’s web interface, in the section with wireless network settings. I wrote about this in an article.
We figured out the reasons, it seems like nothing was missed.
What router is needed to get maximum speed over a Wi-Fi network?
To get maximum speed over Wi-Fi, we need a modern, powerful (and therefore not the cheapest) router New device (laptop, PC with Wi-Fi adapter, phone, tablet, TV) with modern Wi-Fi module. And preferably a provider with a Static IP or Dynamic IP connection protocol.
If we are talking about modern, wireless network equipment, then it goes without saying that there must be support for the 5 GHz band and the . This support should be both in the router and in the device itself that we connect to the Wi-Fi network. That is, the router must be dual-band. You can read more in the article.

Not only that, according to the 802.11ac standard, the Wi-Fi network speed is much higher (maximum, theoretically possible up to 6.77 Gbit/s) in comparison with the most popular now 802.11n, also in the 5 GHz range (and 802.11ac only works in this range) there is practically no interference.
note on the speed of the WAN and LAN ports of the router. In choosing a router that will reduce the speed as little as possible, we forget that the speed is also limited by the WAN port to which we connect the Internet. And if our tariff rate is 200 Mbit/s, and we installed a router whose WAN and LAN ports can operate at a speed of 10/100 Mbit/s, then it is clear that we will not get more than 100 Mbit/s via cable , nor via Wi-Fi.
If you have fast Internet, more than 100 Mbps, then you need a router with only gigabit ports. This is always indicated in the specifications. Even routers in the mid-price range do not always have gigabit (1000 Mbps) ports installed. Be careful.
Routers supporting the 802.11ac standard are now quite available. There are so many models on the market. The only negative is that Wi-Fi network coverage in the 5 GHz range is slightly less than in the 2.4 GHz range. This is true, I have already convinced myself of this. Not critical, but the signal is weaker.
Someimportant points:
- Dual-band routers distribute two Wi-Fi networks. At 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz. So those devices that do not support the new standard will connect in the 2.4 GHz range. If necessary, you can disable an unnecessary network.
- If you want to squeeze out maximum speed through a Wi-FI router, then do not buy budget models. The more expensive the router, the better the hardware installed in it. And this means more productivity and speed.
- Don't forget about restrictions on WAN and LAN ports.
- To achieve maximum speed, update your router's firmware and experiment with Wi-Fi settings. Operating mode, channel, channel width.
- Do not forget that the speed of a Wi-Fi connection also directly depends on the quality, performance and characteristics of the Wi-Fi module of the device on which we measure the speed. You can take measurements on different devices, and you will see that the speed will most likely be different.
You can find more tips on choosing a router in the article.
conclusions
Any router will reduce the speed of the Wi-Fi network. The only question is how much. But how much the speed will drop depends primarily on the power of the router, support for new standards, the parameters of the Wi-Fi receiver in the device, and the provider (connection type and speed according to tariff), interference, signal level, etc.
If you are just choosing a router, then I definitely advise you to buy a dual-band one. With support for the new 802.11ac standard. And preferably with gigabit ports. Most likely, your new mobile devices already support 802.11ac. If everything works well, then for PCs and even laptops you can buy USB adapters that support the ac standard. I would also advise not to skimp on the router. It’s better to take a good, modern and powerful model that will be relevant for many years to come, than to change the router after a year, and spend the whole year spitting on low speed.
It is clear that everything here is individual, and a lot depends on the tasks that the router must cope with. But in this article we are talking about choosing a router that can provide maximum performance and minimal speed losses.
You can leave questions in the comments and share your thoughts on this matter. Also write what router you have, what the tariff is, and what the Wi-Fi speed is. Maybe you were somehow able to speed up your Wi-Fi and want to share some useful advice.
Just one request, don’t ask me which specific model to buy. The choice is yours. I wrote above how to choose.
After purchasing and installing a router, the user is surprised to discover that the speed of the Internet connection becomes lower. That is, roughly speaking, the router reduces the speed, and this happens not only on a wireless network (Wi-Fi), but even on a wired local network. Let’s say that when connecting directly to the provider, the speed was 50 Mbit/s. Through the router, the same connection is already available at 40 Megabits. But the most interesting thing is that the speed limit on the router is not observed when it works with another provider (with a lower speed, or simply with a different protocol). Why does this happen, and is it always possible to solve this problem? Let’s try to figure it out further.
Firstly, you need to answer one question: does the router really reduce the speed, or is the problem caused by other reasons? Let's go to the site 2ip.ru/speed/. Press the button "Test".

Note: Other services also allow you to check the speed of your router, for example internet.yandex.ru, or speedtest.net(here you need to select your city).
If, in the presence of a router (connected to the PC via a patch cord), there is a connection, but the speed really differs (by more than 10-20%, with repeated testing), we conclude that it is “to blame” for the low speed - router.
You can estimate how much the speed drops through the router by the quality of IP-TV (if you have one). With a reduced connection speed, the picture may “twitch”, freeze, the image disappears for 1-2 seconds. What is the reason for this phenomenon?
And there may be several of them (that is, reasons).
Reducing speed on wireless Wi-Fi connections

We must consider this type of connection, that is, “wireless”. The speed of the Wi-Fi network itself, that is, the wireless channel (between the PC and the router’s access point) may not be sufficient, even when using the “latest” 802.11 n protocol. If in theory, the speed of a WiFi router is limited to 300 Megabits, then in practice it is rarely more than 75 Mbit/s. When a large number of devices are connected via Wi-Fi, they can also “interfere” with each other.
Conclusion: The WiFi router reduces the speed, more or less - almost always. But “how much” depends on the hardware.
Routing speed
You may notice that the Internet speed through the router is lower or higher, depending on the protocol of the provider. Most routers, for example, can easily handle DHCP or Static IP; we see lower speeds if the provider uses a VPN protocol (and the most “difficult” one is PPTP). The reason for this “dependence” is the insufficient speed of WAN-LAN routing. The main factors here are: the speed of the hardware, and also the optimization of your firmware. Sometimes, the speed through the router is lower just with the “default” firmware (but if you “update” it, everything falls into place). That is, we conclude that “speed” also depends on the firmware.
But most often, when transmitting WAN-LAN packets, the low speed through the router is due to an insufficiently fast central processor (with 240 MHz, for example, you can forget about the VPN protocol). Miracles don't happen. And yet, it should be noted here that some brands of routers have firmware with which everything works perfectly on weak, from a formal point of view, hardware.
Note: When talking about WAN-LAN switching speed, we did not say that this concept also includes WAN-Wi-Fi switching. And the value of WAN-LAN switching speed is also measured in Megabits/s.
The Internet speed through the router, in any case, cannot be greater than the speed of WAN-LAN switching (which is tested on a given protocol and in a specific router model).
Test results for most common models are posted on the website www.smallnetbuilder.com(site tab LAN-WAN -> Router Charts).

Number of simultaneously open connections
Even if only one PC or laptop is connected to the router, the low Internet speed through the router may be due to too many connections. The fact is that any program, any process (even “hidden”) can create a connection. And not just one, but several.
Solving the problem is easy. Let's say in u-Torrent - go to “settings”:

In parameters "Speed", we see the number of simultaneously created connections. This parameter can be changed.
Question: why without a router - did everything work correctly?
Answer: The fact is that on the other side, the provider also has its own router. Only - different (maybe Cisco, or something similar), that is, faster. Such routers have completely different processors. Their throughput is also different.
The maximum number of connections was increased - and the Internet speed through the router dropped (whereas, without a router, the effect is invisible). For different router models, this parameter (100 or 200) will be different. The faster the processor in the device (and the better the firmware) - the more connections can be opened without reducing the speed.
Adviсe
If you find that the slowdown in Internet connection speed is due to your router, then what should you do? For example, how to increase the speed through a router if it is not sufficient, even with a small number of connections?
We do not consider such an option as “replacing the router”. It is better to remember that the low speed through the router is not only due to the low speed of the hardware installed in it. But also by other factors (for example, firmware).
Perhaps updating the firmware (to a “newer” version) is one of the good options for solving many problems. Each new version of proprietary software is often faster. When asked how to increase the speed of your router, we answer: update the firmware. It is better, in this case, to read the reviews, because the “newest” may be a “beta version”, lacking the necessary stability.
Tip number two. If necessary, and there is such an opportunity, change the provider. Even the most “ancient” equipment works well with the DHCP protocol, or PPPoE (on a static IP address). They complain that the speed through the router dropped when the provider started working via VPN. There is nothing surprising here - and, in this case, you will have to refuse anything (a router, or the services of a provider).
Separately, I must say about Wi-Fi. Let's say that at a short distance from the access point, the speed is the same, but as you move away, it decreases. This is quite expected.
As the distance increases, the intensity of the wave decreases, moreover, in proportion to the square of the distance. Add to this reflections from “conductive” surfaces, and diffraction from a metal grid in the walls - this is the answer to the question why the speed through a router is lower in the case of a wireless connection.
Sometimes, it makes sense to switch the access point to a slower protocol (for example, 802.11 g). Which additionally relieves the processor in the case of a large number of connections. There is no need to change anything in the settings of mobile devices (how to limit the speed on a router - see the setup instructions, most often this is the main block of Wi-Fi parameters):

Well, the encryption mode ( WPA, WPA2) - reduces the speed “by itself”.
Why does the router slow down? Because it is not fast enough, but relative to the conditions in which it must work.
Methods for “improvement” are divided into two classes. Or, we change the “conditions” (the number of open connections, or - more importantly - the communication protocol with the provider). This is one class. Or we change the firmware.
Simple adjustment of the router speed - changing some parameters that affect the speed of operation. For example, if the connection is DHCP, then it is recommended to explicitly specify DNS addresses:

This is the advice that is given most often on forums. How to increase the speed of a router by changing less “significant” parameters should be considered for each model separately.
Let's figure out why Internet speed drops sharply and how it can be increased. Unfortunately, no specialist can give a definite answer to this question. The thing is that the speed of data transfer over the network is influenced by many factors.
All reasons can be divided into two groups: those that depend on you and those that do not depend on you. You can fix the first ones yourself; to solve the second ones, you should call a specialist. Let's look at the main reasons why problems arise when using the Internet?
Reasons up to you
All the reasons that you can influence and eliminate them yourself come down to installing programs, setting them up correctly, searching for viruses and checking the router.
Viruses, antiviruses and firewalls
One of the most popular problems is a virus getting into the computer. There are many programs that allow you to fully track your actions: transitions, entering passwords, reading personal information, etc. For this reason, the Internet speed may drop to zero; if the virus is not removed, the computer as a whole may slow down.
Algorithm for solving this problem:
- install an antivirus program;
- scan your computer for threats;
- remove all detected viruses;
- configure the program so that it works constantly and does not allow viruses to enter your computer.
Often the reason for slow loading of traffic from the network is the antivirus itself, as well as its firewall.
The program and firewalls check information as soon as it enters the computer. Of course, this negatively affects the speed of downloaded information and the operation of the system as a whole.

For diagnosis you need:
- disable your antivirus program and all firewalls;
- wait a little so that all processes stop exactly;
- check Internet loading speed.
Evaluation result:
- if the speed has not changed, look for another reason;
- if the speed has increased, update the program or install another antivirus.
operating system
In some cases, the Internet is slowed down by the operating system. This is especially true for owners of devices on which various assemblies of operating systems are installed, since in most cases they are of poor quality. Such a system will definitely affect the speed of traffic transmission from the network.
Video: low internet speed. Causes and diagnosis
Router limitations
Perhaps the router you are using is not designed for high-speed data transfer (usually this is written on the box). If you have a wireless router, check its settings - it is quite possible that someone else is using your Internet via wifi (Wi-Fi), reducing your speed when downloading and loading pages.
In the first case, troubleshooting network problems is only possible by purchasing a new, faster router. If your neighbors use your Internet, set a password for wifi.
LAN card
Regardless of whether the network card is detected in the system or not, it may be faulty. Then the Internet starts to slow down and load slowly.
If you are a DSL user, this information is unlikely to be useful to you.. It often happens that a network card is connected and is detected by the system, but the Internet speed slows down.
To check, you need to connect to another computer and measure the speed on it. If it matches your tariff plan, then the problem is in the network card.

Solutions:
- for a computer - you can simply replace the card by buying a new one;
- for a laptop – purchase an external USB card.
You can also set the mode to 10Mbit/s, Full Duplex:
- go to the network card settings;
- go to the Additional tab;
- select the Connection Type or Speed&Duplex section.
This will provide you with stable speed, but will not eliminate the cause, so you should definitely call a specialist.
Why did the Internet speed through the router drop?
Sometimes it happens that, according to the agreement with the Internet provider, the speed should be the same, but in reality it is much lower. The speed of the router is affected, first of all, by the number of active Wi-Fi access points. If there are too many of them, then the speed becomes significantly slower.

Let's consider the possible reasons for the drop in speed:
- the provider has some traffic restrictions;
- the tariff plan may change unexpectedly for the users themselves;
- Network overload often occurs in the evening and at night. There is one way to solve this problem - reboot the router. If the speed is low even during the day, call the operator;
- The device requires flashing. Usually the router starts to “glitch” if it is used for a long period of time. Reflashing the device often corrects Internet problems for everyone;
- problems at the station. Call the operator, report the problem, leave a request and find out when the problem will be fixed;
- problems with communication networks. In this case, the best solution would be to call the company and report low Internet speed.
- There they should tell you why the traffic speed has dropped. If only you have such problems, the company must send a technician who will fix the problem;
the company began working using a new VPN protocol. Then you will have to change your Internet provider, because this protocol does not provide for stability in the supply of traffic. This means that the network speed will depend solely on the time of day. Moreover, as a rule, the number of network access points with this protocol significantly exceeds the permissible norms, which significantly affects the speed.
Unfortunately, there are reasons that an Internet user cannot do anything about. You just have to wait for the problem to be fixed by the provider company. Below are the most common problems that affect Internet speed, but which cannot be solved on your own.
Problems on the line
Bad weather outside the window (wind, snow, thunderstorm) can damage the traffic transmission cable and cause poor Internet speed or its absence completely.
In this case, all that remains is to wait for the company’s specialists to repair the cables. For more accurate information, please contact the provider companies.
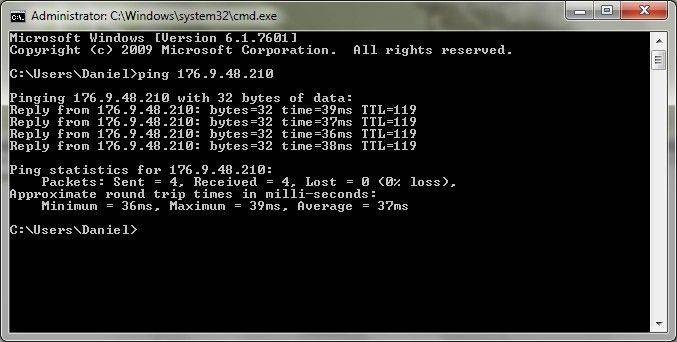
To check your Internet connection speed:
- go to the command line;
- select the ping command;
- put the ping to the gateway in the line, for example ping 11.9.0.2 -t -l 1500, where 11.9.0.2 is the number of your gateway;
- if there are really problems with the connection, you will see the message “The timeout interval for this request has been exceeded.”
Impact of connection type
There are three types of Internet connection:
- cable;
- switched;
It should be remembered that a cable connection will always transfer data over the network faster than the other two types. In addition, the quality of telephone lines also affects the speed of the Internet. Depending on where you live, the speed of your network connection may vary significantly.

External factors
Many people are interested in why the Internet speed drops in the evening; the answer is that the network is overloaded, since in the evening more users watch movies and play games. This causes the speed to decrease. If you encounter a problem at this time, but everything is fine during the day, then this is most likely your reason. Call your Internet provider and report the problem, they may improve your signal.
Testing Internet speed
To check how fast your Internet connection is:
- enter “Test Internet speed” into the search bar;
- The first link is often suitable for a quality speed test;
- The exact number will appear on the dial, which indicates the transfer speed of Mb/s.

If you want to have uninterrupted access to the Internet, carefully read the following recommendations to help make the speed as fast as possible:
- choose a reliable browser that will provide good traffic processing speed. Google Chrome is considered a good browser for surfing the Internet;
- disable advertising in your browser. Displaying it requires a lot of traffic, which is why pages load more slowly;
- install a good antivirus program. It will “intercept” all viruses on the fly and destroy them. This will significantly increase the speed of data transfer over the network;
- Don’t forget to pay for the Internet regularly, otherwise your provider will deprive you of access to the network altogether.
It is quite possible to solve the problem with a slow connection on your own; to do this, you just need to identify the existing problem and find ways to solve it. In this case, the Internet will again delight you with speed and new opportunities!
>In the modern world, it is quite difficult to imagine life without wireless technologies. And this is not strange, because we quickly get used to good things. Today, almost every home has an access point, with the help of which home wireless networks are created. However, every coin has a flip side. And in this article we will talk about why the router often slows down the Internet speed via Wi-Fi and cable.
A little about routers
Does Internet speed depend on the Wi-Fi router? Of course it depends. First, you must understand that there are many different models of routers, both branded and from little-known manufacturers. Such devices differ not only in build quality, signal level and appearance, but also in the components that are used. And the data transfer speed directly depends on this. Therefore, one of the important factors in finding a solution to why the router slows down the Internet speed via Wi-Fi is the quality of the device’s components.

The fact is that the router itself is a mini-computer. And as you know, PC performance depends on the processor, video card, RAM and other components. It’s the same with access points - they use RAM, a processor for signal processing, and all this is installed on the motherboard. Plus, to work with the network, network adapters are used, on which bandwidth also depends.
If you notice that the Internet speed through the router has dropped, then the problem is in its components.
That is, if the provider gives, for example, 100 Mbit/s, but through the router you only get 50 Mbit/s, then the problem is in the router itself. We will return to this topic later and look at how to choose the right access point.
If we talk about a wireless connection, then the low speed through a Wi-Fi router will again be due to the fact that a weak radio module is used. In general, Wi-Fi adapters have different standards, can operate at different frequencies, and so on. All this affects their throughput.
In addition to all of the above, the wireless connection is affected by the signal level - the weaker it is (read: the further you are from the access point), the slower the connection will be. But let's talk about everything in order.
Wi-Fi standards
First, to understand why the router cuts Wi-Fi speed, let's look at what the standards for this wireless connection are:
- 11b is a pretty old mode. With it, the throughput reaches 11Mbit/s. This standard operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. Today it is practically not used. You can only find it on old laptops and the first smartphones with Wi-Fi modules.
- 11g is also an old communication mode, but still more common. As a rule, budget smartphones and outdated laptops are equipped with these modules. Despite the fact that this mode operates at the same 2.4 GHz frequency, the data transfer speed reaches 54 Mbit/s.
- 11n is the new standard. The vast majority of modern access points, laptops and smartphones from the mid-price category to flagship models are equipped with such modules. This mode is universal - some adapters operate at 5 GHz, but most freely available devices still use 2.4 GHz. At the same time, the speed reaches 600 Mbit/s.
From all this we can conclude that if the Internet speed through the router is lower than directly, the reason is precisely the Wi-Fi adapter used. 
Cable connection
And with a cable connection, the explanation why the router reduces the Internet speed over the cable may be in the adapter that is used in the router. As with wireless technologies, cable communications have their own standards. Here are two that are currently in use:
- 3u – Fast Ethernet (fast Internet). The connection of such an adapter is limited to 100 Mbit/s. As a rule, in the vast majority of cases, these are the network cards used on computers and laptops.
- 3z – Gigabit Ethernet (gigabit Internet). The throughput of such adapters can reach 1 Gigabit/s, which is quite a lot, since the vast majority of providers do not provide such speed.
When we talk about network cards, we're not just talking about computers. The fact is that network cards are also used in routers. Therefore, the data transfer speed directly depends on the network card used. Of course, there may be many other reasons why the router does not provide full speed: a lot depends on the settings of the access point, its functionality, firmware, revision (components), and so on. 
Other causes of loss of speed
The answer to the question of whether Internet speed is lost through a router depends on which router is used. We have already discussed some reasons above. But these are not all the factors affecting throughput. The number of simultaneous connections is very important.
The fact is that the system is designed in such a way that when several devices are connected simultaneously, the router evenly distributes access among all subscribers. This means that all traffic is divided by the number of connected devices.
Much determines the correct settings. Then how to configure the router so as not to reduce the speed? The cable connection is not configurable. But with wireless communication, for most router models it is possible to select the Wi-Fi operating standard. That is, you just need to select the fastest mode (802.11n or ac - if supported).
In addition, you need to analyze the congestion of channels and choose the one that is less congested than others. In the “Advanced Settings” section, select “Transmitter Power” (if this function is available). Set the power to 100% (or maximum). There are no other settings that will increase the transfer speed.
How to choose a router

Let's figure out whether all routers reduce speed. No, and it is quite possible to choose a router that will fully meet your requirements, having high throughput.
The main thing is to carefully study the technical characteristics of the device. The cable capacity is always described on the box. And for Wi-Fi, you should pay attention to the wireless connection standard: access points that support the 802.11n standard, as a rule, have a throughput of 150-600 Mbit/s (this is indicated in the technical characteristics).
Of course, you must understand that the cheaper the device, the lower its quality, and the greater the drop in Internet speed through the router. Therefore, you can immediately pay attention to more expensive models. For example, TP-LINK Archer C2 or Asus RT-AC1200G+ router. Their characteristics will necessarily describe the throughput.

So, the answer to the question of which router does not slow down the Internet speed: any one whose characteristics exceed those of your network. When your provider provides you with cable Internet with a throughput of 100 Mbps, you need to choose a router with a throughput of 150 Mbps via cable and with a Wi-Fi connection of the 802.11n standard at a minimum.
At the same time, you should understand that a router that does not reduce Wi-Fi speed will be quite expensive. In addition, the Wi-Fi module on the computer itself must also have high bandwidth.